| 417-01 Exterior Lighting | 2013 - 2014 Fusion |
| Description and Operation | Procedure revision date: 05/10/2013 |
System Operation
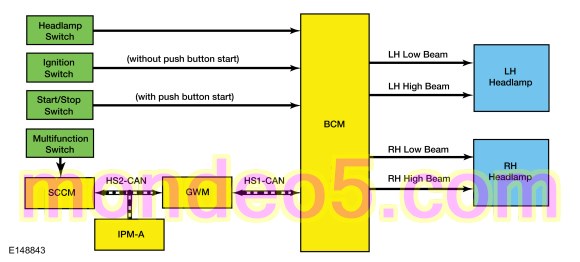
Headlamps
System Diagram
Network Message Chart
BCM Network Input Messages
| Broadcast Message | Originating Module | Message Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Headlamp flash to pass status | GWM | Indicates to the BCM a request for the high beams or flash-to-pass. |
GWM Network Input Messages
| Broadcast Message | Originating Module | Message Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Headlamp flash to pass status | SCCM | Indicates to the GWM a request for the high beams or flash-to-pass. |
SCCM Network Input Messages
| Broadcast Message | Originating Module | Message Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Auto high beam request | IPMA | Indicates to the SCCM a request for the high beams based on the IPMA camera input. |
Low Beams
The BCM monitors the headlamp switch position by sending voltage signals on multiple circuits to the headlamp switch. There is one circuit for each headlamp switch position. At any given time, one of the signal circuits is switched to ground to indicate the headlamp switch position.
The BCM turns the parking lamps and headlamps on when the ignition is in RUN and the BCM detects a fault from the headlamp switch or wiring. This is normal behavior of the BCM when a fault has been detected with the inputs from the headlamp switch.
The BCM also provides an overload protection of the low beam output circuits. When an excessive current draw is detected, the BCM disables the affected low beam circuit driver.
High Beams
The SCCM monitors the LH multifunction switch for a high beam request. When the LH multifunction switch is in the high beam position, the SCCM sends a message through the GWM to the BCM over the High-Speed Controller Area Network (HS-CAN).
When the low beams are on and the BCM receives a request for high beams, the headlamps remain powered on and the high beams are activated. This adds light and changes the headlamp beam pattern to illuminate a greater distance.
The BCM also provides an overload protection of the high beam output circuits. When an excessive current draw is detected, the BCM disables the affected low beam circuit driver.
Flash-To-Pass
The SCCM monitors the LH multifunction switch for a flash-to-pass request. When the LH multifunction switch is in the flash-to-pass position, the SCCM sends a message through the GWM to the BCM over the High-Speed Controller Area Network (HS-CAN).
When the ignition is in RUN and the flash-to-pass is requested, the high beams are activated as long as the LH multifunction switch is held in the flash-to-pass position.
Automatic High Beams
The automatic high beam system uses an interior rear view mirror mounted camera to monitor surrounding traffic conditions and high beam usage. The automatic high beam feature is active only when the headlamp switch is in the AUTOLAMPS position.
The automatic high beams can be enabled/disabled in the IPC message center.
During nighttime driving, if it is dark enough and no other traffic is present, the IPMA sends a message to BCM , through the GWM to turn the high beams on. When the system detects an approaching vehicle's headlamps or a preceding vehicle's rear lamps, the system turns off the high beams. When the approaching vehicle's headlamps or the preceding vehicle's rear lamps are no longer detected, the high beams automatically turn back on.
Headlamp Exit Delay
When the ignition is OFF and the multifunction switch is placed in the flash-to-pass position and released, the parking lamps and low beams are illuminated. They remain illuminated until:
Within the 30 second delay and all the doors closed, opening any door results in the 3 minute timer restarting.
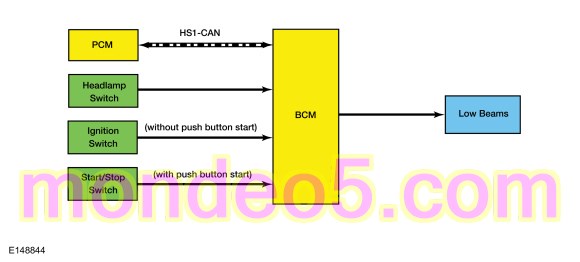
Daytime Running Lamps (DRL)
System Diagram
Network Message Chart
BCM Network Input Messages
| Broadcast Message | Originating Module | Message Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Gear lever position | PCM | Indicates the gear selector lever position to the BCM . When the selector lever is in any position other than park, the BCM activates the DRL . |
Daytime Running Lamps (DRL)
NOTE: The DRL is not a programmable parameter for this vehicle.
The DRL system utilizes the existing circuitry and components from the headlamp low beam system.
The BCM monitors the ignition status, the headlamp switch and autolamp status.
Based on the input, the BCM activates the DRL .
The DRL are activated when the ignition is in RUN and the low beams have not been turned on by the autolamp system or the headlamp switch.
Autolamps
System Diagram

Autolamps
The BCM sends ground and a reference voltage to the light sensor with a voltage signal. The voltage drop on the reference voltage circuit varies with the ambient light conditions.
The BCM monitors the headlamp switch circuits to indicate the headlamp switch position.
When the BCM receives a headlamp switch status indicating a request for the autolamps, the BCM monitors the light sensor for the ambient light condition. If the BCM determines the ambient light level is dark, the BCM supplies voltage to the exterior lamps.
Headlamps On With Wipers On Function
When the headlamp switch is in the autolamps ON position, the exterior lamps turn on when the front wipers are on low or high speed. This feature does not activate the exterior lamps during a mist wipe, while the wipers are on to clear washer fluid during a wash condition or the wipers are in automatic mode.
The exterior lamps turn off when the ignition changes to OFF or ACC mode, the headlamp switch is placed in the off position, or the front wipers are turned OFF. The exception to this is when the exterior lights are on because of darkness determined by the autolamp system.
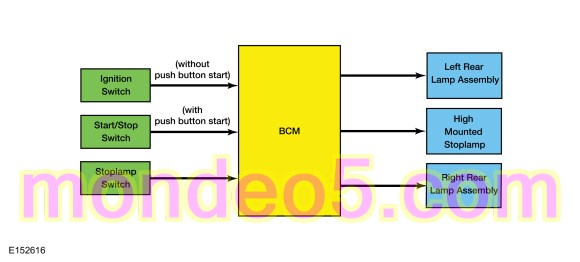
Stoplamps
System Diagram
Stoplamps
The BCM monitors the input from the stoplamp switch. When the brake pedal is applied, voltage is routed to the BCM . The BCM then supplies voltage to the stoplamps.
The BCM does not activate the stoplamps when the ignition is OFF or in ACC mode.
The BCM also provides an overload protection of the stoplamp output circuits. When an excessive current draw is detected, the BCM disables the affected stoplamp circuit driver.
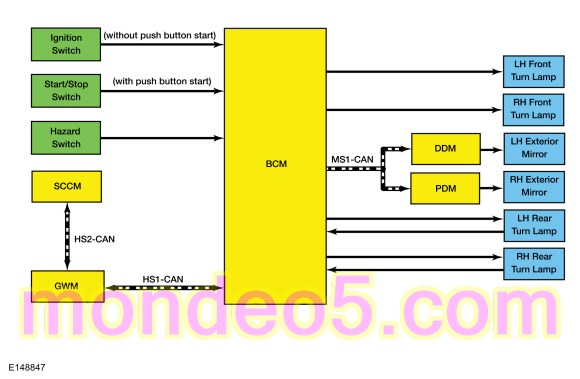
Turn Signal and Hazard Lamps
System Diagram
Network Message Chart
BCM Network Input Messages
| Broadcast Message | Originating Module | Message Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Turn signal switch status | GWM | Indicates the turn signal stalk position on the multifunction switch (left/right lane change or turn signal on or off). The BCM activates the left/right turn signals based on this input. |
GWM Network Input Messages
| Broadcast Message | Originating Module | Message Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Turn signal switch status | SCCM | Indicates the turn signal stalk position on the multifunction switch (left/right lane change or turn signal on or off). |
DDM and PDM Network Input Messages
| Broadcast Message | Originating Module | Message Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Left turn lamp request | BCM | A command to the DDM or PDM to activate/deactivate the exterior mirror turn indicator. |
| Right turn lamp request | BCM | A command to the DDM or PDM to activate/deactivate the exterior mirror turn indicator. |
Turn Signals
The SCCM monitors the LH steering column multifunction switch position. When the LH steering column multifunction switch is in the left or right turn position, the SCCM sends a message through the GWM to the BCM over the High-Speed Controller Area Network (HS-CAN) indicating a request for the left or right turn signal.
When the BCM receives a request for a turn signal, the BCM supplies on/off voltage to the appropriate turn lamps. The BCM sends a turn indicator command message over the Medium-Speed Controller Area Network (MS-CAN) to the door modules for the exterior mirror turn lamps.
The timed on/off cycle for turn lamps is determined by the BCM and is set to flash approximately 70 times per minute if both the front and rear turn signal lamps operate correctly.
The rear turn lamps are Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) in the rear lamp assemblies and have an outage circuit that tells the BCM when the Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) are inoperative. During normal operation, when voltage is applied to the rear turn Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs), the feedback circuit sends the same voltage back to the BCM through the outage circuit. If the Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) are inoperative the BCM will not receive this voltage feedback through the outage circuit.
If a front or rear turn signal lamp is inoperative, the BCM fast flashes the remaining turn lamp(s) approximately 150 times per minute to indicate a bulb outage to the driver.
The LH steering column multifunction has 2 detents for the left turn position and 2 detents for the right turn position. When placed in the first detent and released, the corresponding turn signals flash 3 times and turn off. When the LH steering column multifunction switch is moved to the second detent, the turn signal flashes until the steering wheel is turned in the opposite direction.
The BCM also provides an overload protection of the turn lamp output circuits. When an excessive current draw is detected, the BCM disables the affected low beam circuit driver.
Hazard Lamps
The BCM sends a voltage signal to the hazard flasher lamp switch to monitor for a hazard lamp function request. When the hazard flasher lamp switch is pressed, the voltage signal is routed to ground, indicating a request to activate or deactivate the hazard lamp function.
When the BCM receives a request for the hazard lamps, the BCM supplies on/off voltage to all the turn lamps.
The timed on/off cycle for the hazard lamps is approximately 70 times per minute, regardless of bulb outage.
Parking, Rear, and License Plate Lamps
System Diagram
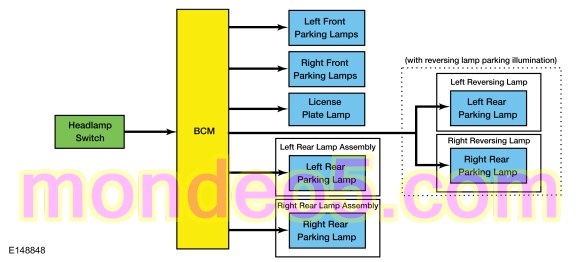
Parking Lamps
The BCM monitors the headlamp switch position by sending voltage signals on multiple circuits to the headlamp switch. There is one circuit for each headlamp switch position. At any given time, one of the signal circuits is switched to ground to indicate the headlamp switch position.
If the BCM detects a fault from the headlamp switch or loses communication with the headlamp switch, the BCM turns the parking and headlamps on. This is normal behavior of the BCM when a fault has been detected with the inputs from the headlamp switch.
When the BCM receives an input requesting the parking lamps on, it provides voltage to the parking lamps.
The BCM also provides an overload protection of the park lamp output circuits. When an excessive current draw is detected, the BCM disables the affected low beam circuit driver.
Fog Lamps
System Diagram
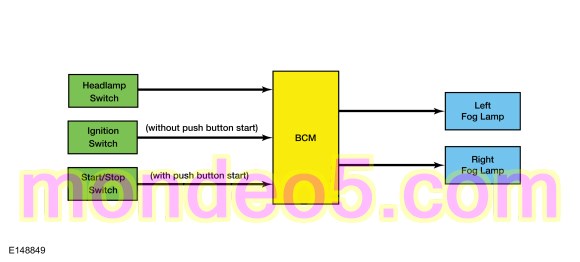
Fog Lamps
The BCM monitors the headlamp switch position by sending voltage signals on multiple circuits to the headlamp switch. There is one circuit for each headlamp switch position. At any given time, one of the signal circuits is switched to ground to indicate the headlamp switch position.
When the BCM receives input from the headlamp switch indicating a request for the fog lamps, the BCM provides voltage to the fog lamps.
The BCM also provides an overload protection of the fog lamp output circuits. When an excessive current draw is detected, the BCM disables the affected low beam circuit driver.
Reversing Lamps
System Diagram
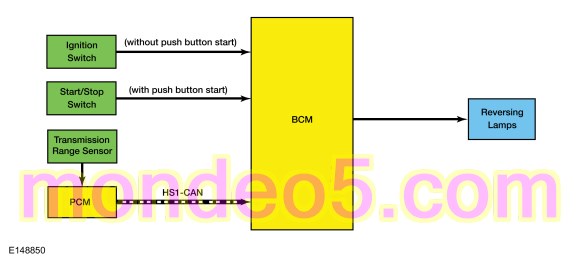
Network Message Chart
BCM Network Input Messages
| Broadcast Message | Originating Module | Message Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Gear lever position | PCM | Indicates the transmission is in reverse gear to the BCM . When the transmission is in REVERSE and the ignition in RUN, the BCM provides voltage to the reversing lamps. |
Reversing Lamps
When the transmission is in REVERSE, the PCM sends a message over the High Speed Controller Area Network (HS-CAN) to the BCM indicating the transmission is in REVERSE. The BCM provides voltage to the reversing lamps when it receives the message that the transmission is in REVERSE and the ignition is in RUN.
The BCM also provides an overload protection of the reversing lamps output circuits. When an excessive current draw is detected, the BCM disables the affected low beam circuit driver.
Component Description
Headlamp Assembly
Exterior lamps are vented to accommodate normal changes in pressure. Condensation can be a natural by-product of this design. When moist air enters the lamp assembly through the vents, condensation can occur if the temperature is cold. When normal condensation occurs, a thin mist forms on the interior of the lens. The thin mist eventually clears and exits through the vents during normal operation. The amount of time it takes to clear the lens of acceptable mist varies with ambient humidity and lamp types. Normal condensation clears from any lamp in 48 hours under dry conditions.
Do not replace a lamp assembly with acceptable levels of condensation such as the presence of thin mist (no streaks, drip marks or droplets are present) or a fine mist covers less than 50% of the lens.
Examples of unacceptable moisture (usually caused by a lamp housing leak) are water puddling inside the lamp or large water droplets, drip marks or streaks present on the interior of the lens.
Light Sensor
The BCM sends a voltage signal to the light sensor. The light sensor provides resistance between the voltage signal and ground. The resistance varies depending on the amount of ambient light detected by the light sensor. The brighter the ambient light, the lower the resistance. By varying the resistance, the BCM can determine the amount of ambient light.
Stoplamp Switch
The stoplamp switch is a normally open switch and is provided voltage at all times. When the brake pedal is applied, the switch closes and routes voltage to the BCM .
Copyright © Ford Motor Company